Redefining Developmental Math for Non-Algebra Core Math Course
Dr. Daryl Stephens (stephen@etsu.edu) and
Murray Butler (butlern@etsu.edu)
East Tennessee State University
Presented at Tennessee Mathematical Association for Two-Year Colleges conference, Blountville, TN, April 18, 2008
Disclaimers
• We don’t have all the answers.
• We don’t even have all the questions!
• Your mileage may vary. (It may be that nothing in this presentation will apply
to your institution’s situation.)
ETSU’s Situation (Here’s where your mileage may vary.)
• About 90% of our students do NOT take an algebra-based
course (such as college algebra, precalculus, calculus) for graduation. These
students take MATH 1530, Probability and Statistics, as their core math class.
• Very little intermediate algebra is used in this course.
• Mostly majors in math and the sciences take something other than prob & stat
for graduation, and they are required to take one semester of calculus. (Digital
media majors take both P&S and trig.) These students benefit from intermediate
algebra.
• NSTCC and WSCC are affected by ETSU’s decisions.
Our Redesign Proposal -- What did we think we would do?
• Re-vamp DSPM 0800 to make it a better preparation for
statistics
• Delete DSPM 0850 requirement for students not taking precalculus or other
algebra-based courses
Same Topics, New Sequence
• What concepts do the statisticians think the incoming students need?
Emphasize:
• Order of operations, especially distributive property, even when using a
calculator
• Comparing (order) fractions, decimals, percents, and signed numbers
• Interpret numerical answer—(what does it mean?)
• Estimation: does the answer make sense?
• Percent, proportions, decimals
• Solving and graphing linear equations
• The language of inequalities
Our Proposal – Technology
• Use My Math Lab, Hawkes Learning, or similar programs with both courses
• Alternate days between lecture classroom and computer lab as is done with
statistics course
• Do spreadsheet activities in elementary algebra to prepare students for
Minitab
• Use graphing calculator in elementary algebra to prepare for stat and in
intermediate algebra to prepare students for precalculus
• Envisioned Advantages
• Cost savings: Cut back on sections of 0850 from ~12 each semester to ~3 or 4.
• Prepare students for courses they would actually take
• More individualized help with computer programs and developmental math tutors
Disadvantages
• Administration would be difficult
• What about students who placed in 0850? Move them on in to 1530 or put them in
0800?
• What about students who change to science major after finishing 0800→1530?
TBR DSP Redesign
• Subcommittees working in all areas including math
• Align with Tennessee high school exit standards
• This year’s 7th graders (Class of 2013) will have to take math all 4 years of
high school!
• New math curriculum standards based on NCTM, ADP, ACT, NAEP, . . .
Math Redesign Subcommittee
• Subcommittee includes university, community college, and high school faculty
• Currently surveying math and other faculty across TBR to see what math is
actually needed in intro and gen-ed courses
• Some thought given to multiple exit points
• More questions than answers at this point
Committee’s Charge
• Examine what should be taught, when, and why.
• Pilot programs help decide who, how, and where.
Subcommittee Members
• Chris Knight (Walters SCC) Co-chair
• John Kendall (SW TN) Co-chair
• Marva Lucas (MTSU)
• Helen Darcey (Cleveland SCC)
• Mary Monroe-Ellis (PSTCC)
• Sharon Lee (Wilson County Schools)
• Daryl Stephens (ETSU)
MATH Survey
• The next few slides show a version of some questions that may be on the
questionnaire to ask what math is needed in TBR core math classes with a
prerequisite below the level of MATH 1xyz.
• MATH 1010, 1110, 1130, 1410, 1420, 1530, 1630, 1710, 1720, 1730
• Integrated Concepts
1. Connecting mathematics to other disciplines (real world applications)
2. Connecting mathematics symbolically, numerically, graphically and verbally
(Reading and interpreting graphs and tables, communicating mathematics,
modeling)
3. Integrating technology (as a tool for problem solving and discovery)
4. Developing study skills (problem solving strategies, managing math anxiety,
time management, feasibleness of solutions)
5. Analyze characteristics of functions (including domain, range, increasing,
decreasing, and continuity)
• Math Skill List
1. Algebra and Number Sense
o Perform operations on real numbers
o Perform operations on complex numbers
o Perform operations on polynomials (including factoring)
o Analysis of linear functions and graphs (including inequalities)
o Solve linear equations/inequalities
o Analysis of quadratic functions and graphs (including inequalities)
o Solve quadratic equations/inequalities
o Analysis of rational functions and graphs (including inequalities)
o Solve rational equations/inequalities
o Analysis of radical functions and graphs (including inequalities)
o Solve equations/inequalities with radical expressions
o Analysis of exponential and logarithmic functions and graphs
o Solve exponential and logarithmic equations
o Unit conversions (mass, weight and volume in both standard and metric systems)
o Solve systems of equations and inequalities
2. Introductory Probability and Statistics
o Basic probability
o Applying descriptive statistics ( of center and variation)
o Organize and display data ( histograms, stems and leaf, pie charts, scatter
plots)
3. Geometry
o Geometric principles ( parallel line and transversals, sum of angles in plane
figures, distance formula, midpoint formula, volume, and surface area)
Questionnaire for Non-Math
• Please list the top prerequisite math skills needed in your program or
course. Only include those courses that do not already have a math prerequisite/corequisite.
In other words, what math skills do your students need to have before they enter
your class to have a reasonable chance at success?
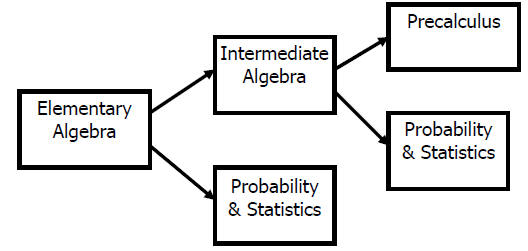
What to do now?
• Find money and/or share computer space
• Move forward with the changes we can make
1. Teach the important topics that prepare students for statistics in our DSPM
0800, then move students straight to Statistics
2. Students needing Precalculus take DSPM 0850
Proposed Sequences
DSPM 0800 Content (proposed)
(Based on Martin-Gay combined 4th edition)
1. Review of Real Numbers
1.2 Symbols and Sets of Numbers
1.3 Fractions
1.4 Introduction to Variable Expressions and Equations
1.5 Adding Real Numbers
1.6 Subtracting Real Numbers
1.7 Multiplying and Dividing Real Numbers--Operations on Real Numbers
1.8 Properties of Real Numbers
2. Equations
2.1 Simplifying Expressions
2.2 The Addition and Multiplication Properties of Equality
2.3 Solving Linear Equations
2.4 An Introduction to Problem Solving
2.5 Formulas
2.6 Percent
2.8 Linear Inequalities
3. Graphing
3.1 Reading Graphs & the Rectangular Coordinate System
3.2 Graphing Linear Equations
3.3 Intercepts
3.4 Slope and Rate of Change
3.5 Slope-Intercept Form: y = mx + b
3.7 Functions
4. Systems of Linear Equations
4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing
Integrated Review – Solving Systems of Equations
5. Exponents and Polynomials
5.1 Exponents
9. Inequalities and Absolute Value
9.1 Compound Inequalities
9.4 Linear Inequalities in Two Variables and Systems of Linear Inequalities
10. Radicals, Rational Exponents
10.1 Radicals and Radical Functions
Appendices
D. An Introduction to Using a Graphing Utility
G. Mean, Median, and Mode
Proposed New DSPM 0850
5. Exponents and Polynomials
5.1 Exponents
5.2 Polynomial Functions and Adding and Subtracting Polynomials
5.3 Multiplying Polynomials
5.4 Special Products
Integrated Review - Exponents and Operations on Polynomials
5.5 Negative Exponents and Scientific Notation
5.6 Dividing Polynomials
5.7 The Remainder Theorem
6. Factoring Polynomials
6.1 The Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping
6.2 Factoring Trinomials of the Form x^2 + bx + c
6.3 Factoring Trinomials of the Form ax^2 + bx + c and Perfect Square Trinomials
6.4 Factoring Trinomials of the Form ax^2 + bx + c by Grouping
6.5 Factoring Binomials
Integrated Review-Choosing a Factoring Strategy
6.6 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring
6.7 Quadratic Equations and Problem Solving
7. Rational Expressions
7.1 Rational Functions and Simplifying Rational Expressions
7.2 Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
7.3 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions with Common Denominators and
Least Common Denominator
7.4 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions with Unlike Denominators
7.5 Solving Equations Containing Rational Expresions
Integrated Review-Summary on Rational Expressions
7.6 Proportion and Problem Solving with Rational Equations
7.7 Simplifying Complex Fractions
10. Radicals, Rational Exponents, and Complex Numbers
10.2 Rational Exponents
10.3 Simplifying Radical Expressions
10.4 Adding and Subtracting and Multiplying Radical Expressions
10.5 Rationalizing Denominators and Numerators of Radical Expressions
Integrated Review - Radicals and Rational Exponents
10.6 Radical Equations and Problem Solving
10.7 Complex Numbers
11. Quadratic Equations and Functions
11.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
11.2 Solving Quadratic Equations by the Quadratic Formula
11.3 Solving Equations by Using Quadratic Methods
Integrated Review-Summary on Solving Quadratic Equations
11.5 Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs
11.6 Further Graphing of Quadratic Functions
4. Systems of Linear Equations
4.2 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution
4.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Addition
Integrated Review - Solving Systems of Equations
4.5 Systems of Linear Equations and Problem Solving
*12. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions (optional)
12.1 The Algebra of Functions: Composite Functions
12.2 Inverse Functions
12.3 Exponential Functions
12.4 Logarithmic Functions
12.7 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations and Applications
This presentation will be on Daryl’s faculty web page: http://faculty.etsu.edu/stephen/handouts.htm Look for links from that page.
Contact Information:
Mailing address for both: Department of Mathematics, East Tennessee State
University, Box 70663, Johnson City, TN 37614-1701


